This article is about deficiency symptoms in aquarium plants. In practice, sometimes these deficiency patterns cannot be clearly and easily recognized, since the symptoms can be very similar to each other and the deficiencies and defects can be very similar. However, the following list should provide an overview of how to recognize them, ordered by the importance of individual nutrients.
HOW TO KNOW WHAT NUTRIENT DEFICIENCIES WE HAVE
In the article How to fertilize a Planted Aquarium We have already presented the most important nutritional resources for healthy growth of aquatic plants, which are, in short, light, carbon, macronutrients and micronutrients. In accordance with the Law of Minimumsa subscriber routine Complete is essential for plants to grow vitally.
If the growth of aquarium plants is stunted, or even show damage to their tissues, they generally suffer from lack of nutrients or imbalances in the aquarium. It is not uncommon for these factors to appear in combination with increased algae growth.
CO2
In the event that any deficiency in aquatic plants, who plants don't grow or let's see that aquarium plants are in poor condition You should first evaluate the amount of carbon dioxide you add to the water before dealing with the other nutritional factors. Most of the patterns presented below, such as yellow leaves or stunted growthThey can also be caused by a carbon deficiency. CO2 fertilization is essential for the healthy growth of plants. In a densely planted aquarium, the CO2 content should be at a level of about 20 to 30 mg / l. This must be permanently monitored with a Dropchecker. Regularly changing the indicator fluid is important for the test to work properly, every four to six weeks is recommended.
If you can rule out the lack of CO2 you should address the following issues.
MACRONUTRIENTS
Macronutrients are nutrients that plants need in large quantities. Mainly, it includes the elements like potassium, phosphorous and nitrogen, but also magnesium. Next, we will go into detail about the most important macronutrients and the most common deficiency symptoms.
LACK OF NITROGEN
Nitrogen (N) can be absorbed by aquatic plants in various forms: ammonia, urea, and nitrate. To determine the nitrogen content of the water, we generally only have water tests capable of indicating nitrogen in the form of nitrate (NO3). Optimal concentrations are around 10 to 25 mg / l NO3.
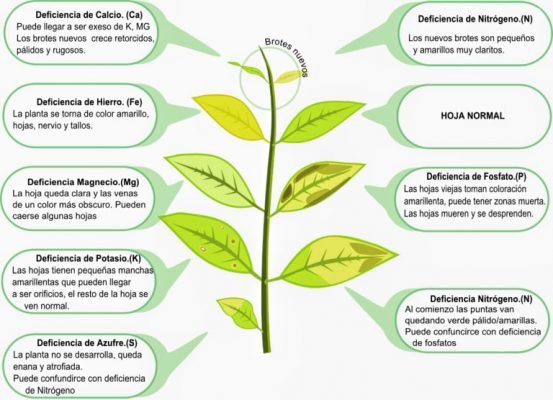
A typical symptom of a nitrogen deficiency is a general yellow coloration of the plant, especially on the older leaves. New leaves getting smaller or stunted growth may also be an indication of a nitrogen deficit. Some plant species assume a clearly reddish hue. An increased presence of green filamentous algae, brush algae, or black beard is quite common when the aquarium lacks nitrogen. You can increase the nitrogen supply with liquid fertilizers like QUALDROP N Green without notably influencing other nutritional elements.
LACK OF MATCH
The concentration of this element in water is normally measured by taking the concentration of phosphate (PO4). This is done with a standard water test available in stores. The symptoms of a phosphorus deficiency (P) can be easily seen on fast growing stem plants. He very slow growth and the tips of the shoots decrease in size they are the most common bioindicators.
Some aquatic plants can become darker or even violet in color. Often a phosphate deficiency May cause an increase in green dot algae. In a planted aquarium, phosphate concentrations of approximately 0.1 to 1 mg / l PO4 are recommended. This substance does not need to be measurable and kept permanently in the water. Phosphate is quite reactive and can interact with other nutrients like iron. Furthermore, the plants can store phosphate really good. A excess phosphates in the aquarium can result in the appearance of filamentous green algae. With this in mind, fertilization alternates with a phosphate fertilizer such as QUALDROP P Grow a few times a week has proven to be sufficient.
LACK OF POTASSIUM
Common for lack of potassium (K) are the sheets with holes or dying leaf tissue (necrosis). At first, a potassium deficit they only show up as little black dots, but then they become visible perforations, which are partially outlined in yellow or black, similar to a nitrogen deficiencyThese bioindicators can be shown in Anubias, Hygrophylas and Ferns, in addition, the leaves can turn yellow and show reduced growth. He excess potassium in aquarium plants can block the absorption of other nutrients to plants, the new leaves also grow twisted and stunted. Optimal potassium concentrations are around 5 to 10 mg / l in water. You can fertilize this item accurately with a potassium only fertilizer like QUALDROP K Clarity.
LACK OF MAGNESIUM
Magnesium (Mg) plays an important role in photosynthesis, because forms an important part of the green pigment (chlorophyll) of the plant. A deficiency of this element is often shown by a pale or yellow discoloration of older leaves, while the leaf veins generally remain green. Magnesium is still a fairly underrated nutrient in planted aquariums. If you want to fertilize magnesium in the aquarium, you can use the fertilizer QUALDROP MG Up.
LACK OF MICRONUTRIENTS
Micronutrients are elements that plants only need small amounts (for the most part only as trace elements) for its proper growth. The most important of them is iron, but also other metals such as copper, boron or manganese. When you use a micronutrient fertilizer like QUALDROP Trace Plant generally all of these are covered.
LACK OF IRON
When a lack of iron (Fe), plants will produce less chlorophyll in their new shoots. An iron deficiency is easily identified at the tips of the shoots of fast growing stem plants. The leaves are no longer green, and the shoots of young plants acquire a color that ranges from yellow to white and transparent. (chlorosis).
In the case of a severe iron deficiency, you can also present the stunted growth and dying black leaf tissue (necrosis). Deficiency symptoms can be easily remedied by adding a little more iron fertilizer. You can add more iron with a fertilizer indicated for this as QUALDROP FE Hybrid.
The ideal iron concentrations for planted aquariums are from 0.05 to 0.1 mg / l Fe, which can be verified with an iron test. However, it is not absolutely necessary to permanently maintain a measurable iron concentration. Iron can only be measured just after fertilizing. After a couple of hours, the nutrient may not be detectable as aquatic plants absorb it very quickly due to its easy availability. As long as there are no typical deficiency symptoms, there is no need to increase iron fertilization. Conversely, overfertilization can promote the growth of red algae such as deer horn or beard algae. However, these can be removed quite easily by taking the appropriate measures.
OTHER TRACE ELEMENTS
Normally, micronutrient fertilizers full too meet the needs of other essential trace elements. In planted aquariums, these trace elements and their deficiency symptoms receive no special attention. Lack of carbon, iron or macronutrients is much more likely than this and therefore needs to be addressed first.
LIGHT
Lack of light is rare in a balanced system. But could be one of the causes of the slow growth of plants. A more nutrient-focused look at points 1 to 3 should have a much higher priority. The lighting requirements of the plants must coincide with the technical conditions of the aquarium. A symptom of mild deficiency may beEg extremely slow growth. Many plant species prefer a lot of light, like most stem plants, but also some ground covers that tend to glean in low light and the plant develops very long internodes. The distances between two stem knots are too long as the plant tries to reach the surface for more light. Stronger lighting ensures more compact growth, but it is also important to adjust the supply of carbon dioxide and the macro and micro nutrients. Increased light acts as a catalyst for plant growth and leads to increased nutrient intake. If the reserves are not replenished, this could cause an imbalance and increase algae growth. In some cases it may be that the position of a given group of plants is entirely optimal. Poor lighting in certain areas of the aquarium or excessive shading by other plants or decoration are the most common causes.
THE RIGHT PERSPECTIVE
To consider deficiency symptoms in aquatic plants You must take into account that certain optical factors can influence. It may happen that you see deficiency symptoms on your plants even though there is no reason. The color of the light source influences how you perceive the colors of your aquatic plants, such as green leaves. Light sources with a daylight spectrum of approximately 6500 Kelvin are neutral. Some pure white LEDs make the bright greens look very pale and whitish. This could be misinterpreted as chlorosis. In contrast, LED lamps with higher RGB content enhance red shades, which look much less dramatic in more neutral light. Another important factor is the angle of incidence at which a plant is examined underwater. Viewed from above through the water's surface, light green hues also tend to look much paler than the same plant through the front glass.
Other articles of interest may be:
How to Eliminate Aquarium Algae - Causes and Most Effective Treatments
Caridines and Neocaridines - File and Care Aquarium Prawns
Rate this post:
In our online store you can buy Items for Gambario and receive them within 24 hours in Spain.
Buy Gambario Items






























